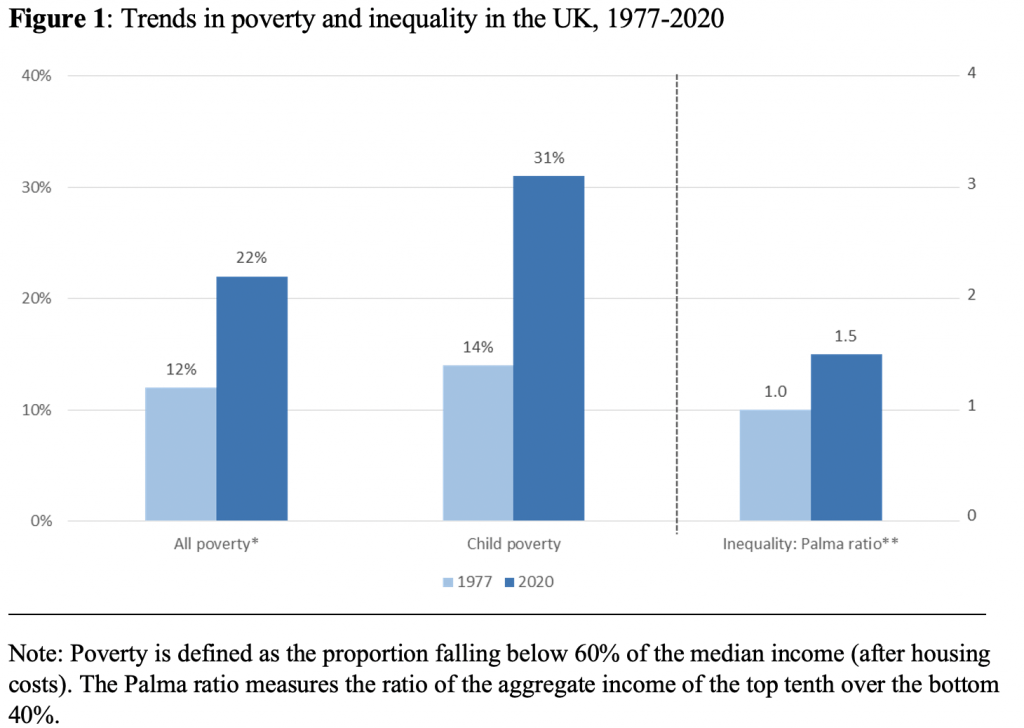
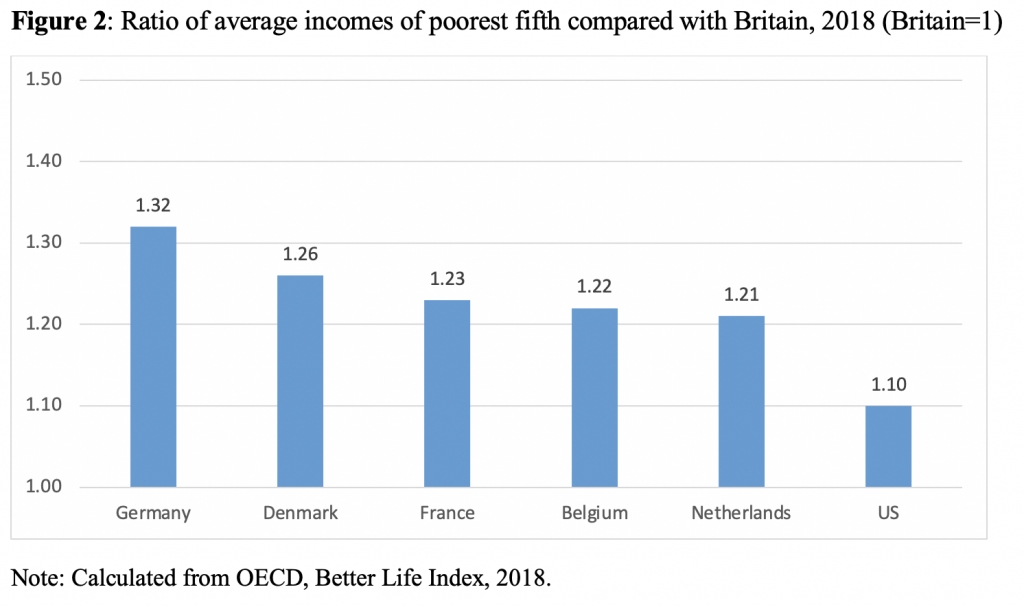
The government’s levelling-up plan dodges the hard choices says Henry Overman. Countering the economic forces behind the UK’s spatial disparities requires addressing multiple barriers and allowing differing approaches – and the funds committed so far don’t appear to be proportionate to the scale of the challenge.
The government’s Levelling-Up White Paper focuses on 12 missions that aim to level-up the UK. Lots will be said about whether the government is spending enough (almost certainly not), whether devolving more powers is a good thing (almost certainly), and how much of their plan is different to past efforts (not much, for those of us that remember the 1990s and 2000s).
Setting these issues aside, does the economic strategy make sense? If government spent enough, and gave places the right powers, would pay, employment and productivity gaps narrow? The answer will depend on how government resolves the fundamental tension between the role of ‘globally competitive cities’ (part of mission 1) and other local economies spread across the country. For the economic strategy to work, the evidence suggests that spatially concentrated investment is crucial, but politics and a concern for quality of life make the case for equalising spending.
Many things determine spatial disparities in Britain. The legacy of 1970s deindustrialisation, the ongoing shift from manufacturing to services, and falling communication and transportation costs all play a part in changing the geography of jobs and the demand for different types of workers. Spatial differences in educational attainment, the selective migration of skilled workers and differences in amenities and costs of living help determine the supply of different types of workers. Demand for and supply of skills interact in a way that can be self-reinforcing, meaning large spatial differences can emerge and persist. Levelling-up policy must counter these economic forces if it is to succeed.
One important consequence of these economic forces is that spatial disparities in earnings – which the government wants to narrow – largely reflect the concentration of high-skilled workers. The share of adults with degrees ranges from 15 per cent in Doncaster to 54 per cent in Brighton. High-skilled workers tend to work in better performing labour markets, which further magnifies individual labour market advantages. At least 60 per cent and up to 90 per cent of differences in average wages across areas can be attributed to differences in the types of people who work in different places.
This has important consequences for ‘levelling up’. A pragmatic aim for the economic strategy might be to improve economic performance in some areas outside of London and the South-East – reducing spatial disparities at the regional level, if not necessarily across more narrowly defined local areas. This would allow talented young people in left-behind places to access better paid opportunities without having to move across the country.
To generate these opportunities and counter the self-reinforcing feedback loops – which mean the highest paid jobs are concentrated in London and a handful of other areas – large investments will be needed in a limited number of cities to attract high-skilled workers and the firms that employ them. The mention of globally competitive cities (as part of mission 1) suggests that the government understands this key point.
Why focus on the high-skilled? Because the evidence – much of which is discussed in a report on spatial inequalities by myself and Xiaowei Xu, written for the IFS Deaton Review – suggests that the impact of targeted R&D investment(mission 2), infrastructure (missions 3 and 4), public sector relocation and other place-based policies will be small unless they significantly alter the composition of the workforce in an area. Even a project of the size of HS2, for example, will do little for the economy of the West Midlands unless it somehow improves local educational outcomes for children growing up there or encourages a much larger share of graduates and the firms that employ them to locate there.
And why cities, not towns? Such investments could improve earnings in any area. However, there are many small towns, investment in infrastructure and innovation is costly, and there are only so many public sector jobs to relocate. Focusing on towns, especially with limited funds, does not scale up to produce large effects across lots of areas.
Looking to cities recognises that the advantages of high-skilled areas are self-reinforcing. The concentration of high-skilled firms and workers generates productivity advantages for firms and better labour market outcomes for workers. In turn, this attracts high-skilled workers from across the country. In short, London’s economic advantages stem from the concentration of skilled firms and workers, and from its economic size, and these factors are self-reinforcing. London’s economic strength also spills over to benefit towns and cities across the wider South-East.
To provide a counterbalance to London and the South-East, investment needs to kick-start these self-reinforcing processes elsewhere. The fact that size is one key part of this self-reinforcing cycle explains why that investment needs focusing on cities.
Unfortunately, we need to recognise that these policies are likely to benefit high-skilled workers more than low-skilled workers. For talented children growing up in struggling towns, increased opportunities nearby offer the option of commuting or a small-distance move, making it easier to maintain links with family and friends. Moreover, some of these benefits will trickle down to the lower-paid in the form of moderately higher wages and improved employment rates, but at the cost of expensive housing.
Sadly, while all these trickle-down benefits are possible, London – with its many poor neighbourhoods, expensive housing and high poverty rates – points to the limits of this approach for improving outcomes for those at the bottom of the income distribution. A more equal spread of graduates – and globally competitive cities in each region – may help reduce spatial disparities and may even help improve the overall performance of the economy, but it is no simple fix for improving outcomes for poorer households. To do this, complementary investments must make sure that households can access the opportunities generated.
The current debate often interprets this as being about ‘better transport’. For many poorer households, however, transport investment generally will not be enough. Again, examples from London illustrate the issues – Barking and Dagenham (areas in the east of London) have good transport links to one of the largest concentrations of employment in the world, but this is not enough to prevent low earnings for many households who live there. If poorer households are to benefit from the kind of investments described above, then they will need help to improve their education and skills.
For some households, the multiple barriers that prevent individuals from being able to access better economic opportunities go beyond education and skills. Many of the ‘left-behind’ places that levelling-up wants to target have high proportions of vulnerable people with complex needs and low levels of economic activity. This compounds their problems, as long-term unemployment, poverty, mental illness and poor health often go hand-in-hand.
Addressing these multiple barriers will involve significant investment not only in education and skills, but also in childcare, and in mental and physical health services. Research suggests that small tinkering and minor tweaks of existing policies will not be enough to tackle the multiple barriers faced in these places. The White Paper recognises these issues with its focus on education (missions 5 and 6) and health (mission 7), but the funds committed so far do not appear to be proportionate to the scale of the challenge.
I have focused on the economics of levelling up but it is important to be clear that spending on levelling-up does not always need to be justified based on economic growth. There are important public good arguments that can justify increased expenditure across a wide range of policy areas. And unlike the economic strategy, there is a strong case that these funds should be equally distributed. For example, it is possible to argue for subsidising rural broadband (part of mission 4) as a public good, while recognising that its economic impacts are likely to be limited. In addition, although such policies, including those around wellbeing (mission 8), pride in place (mission 9) and crime (mission 11) do not specifically target the bottom of the income distribution, they will often benefit poorer households most.
Places matter to people. For many people, the place where they grow up will become the place where they live and work. Disparities in economic opportunities, in costs of living and in amenities provide the context for, and directly influence, the decisions they take and the life they will live.
Improving economic performance and helping to tackle the problems of left-behind places are both important policy objectives. Addressing these challenges requires a new approach to policy, one that allows for different responses in different places. Such variation makes many people nervous. Constituency based politics mean that political messages tend to prefer spending everywhere. However, policy must allow for this variation. Devolved power (mission 12) will help but central government will still need to grapple with the fundamental trade-off between concentrating spending to help achieve the economic strategy while spreading out spending to meet the other objectives.
I would argue that this becomes easier if we remember that we should care more about the effect of policies on people than on places. If this is the case, we should judge the success of levelling-up on the extent to which it improves individual opportunities and on who benefits, rather than on whether it simply narrows the gap between places.
___________________
About the Author
Henry Overman is Professor of Economic Geography in the Department of Geography and Environment at the London School of Economics and Director of the What Works Centre for Local Economic Growth. He is Research Director of the Centre for Economic Performance.
https://blogs.lse.ac.uk/politicsandpolicy/levelling-up-the-governments-plans-arent-enough-to-promote-economic-growth-and-tackle-inequality/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=email